The goal of this work was to tie the Hipparcos stellar coordinates to the inertial frame of the distant radio quasars (VLBI sources). This tie was to align the optical and radio coordinate systems at the milliarcsecond level to make possible registration of radio and optical images. At the eve of this projet , in 1982, we selected 11 stars that could be observed both by Hipparcos and VLBI; they were brighter than magnitude 12 to be observed by the satellite Hipparcos; they were radio-emitting in the non-thermal regime (gyrosynchrotron) to be compact enough to match the high angular resolution of VLBI. The comparison of the coordinates and proper motions measured by Hipparcos and VLBI for these 11 link stars yields straightforwardly the 3 rotation angles, and their rates, between the Hipparcos and VLBI extragalactic spheres.
The weak radio flux density (usually < 20 milliJansky) of these stars was a challenge at the beginning of the 80's for the VLBI technique. This was the combination of the phase-referencing technique, of the MarkIII wide-bandwidth VLBI data acquisition system of Haystack Observatory and of the use of the large radiotelescopes (64 m then 70 m) of the NASA Deep Space Network and of the NRAO phased VLA (125 m), that provided enough sensitivity and astrometric accuracy (1 milliarcsecond or better per observation) to successfully complete this project.
I have carried out this work at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Pasadena) in the VLBI group headed by Robert A. Preston in close collaboration with Haystack Observatory (MIT, Boston). My collaborators on this project have been R.A. Preston, D. Gabuzda, D. L. Jones of JPL, A.E.E. Rogers, R.B. Phillips, M. Titus of Haystack Observatory and R.L. Mutel of Iowa University.

|
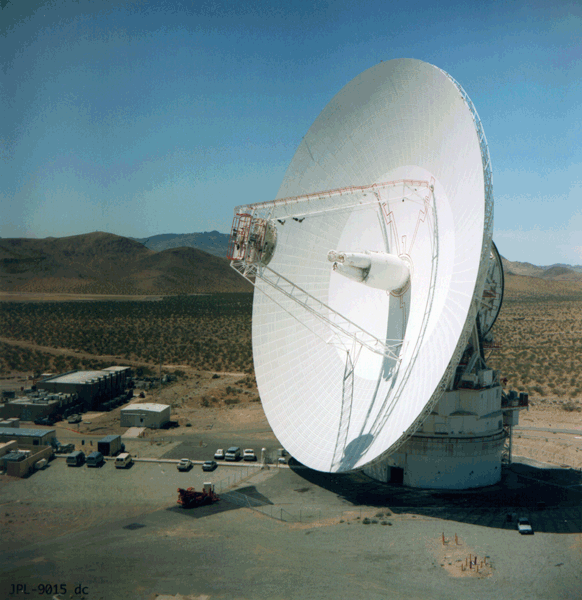
The NASA Deep Space Network station DSS14 at Goldstone near Barstow in California, 64 m in diameter at the beginning of the project and 70 m after 1987, has been the key antenna along with the phased-VLA to provide enough sensitivity for the VLBI arrays at 8.4 GHz (3.6 cm) used in the course of the project. |
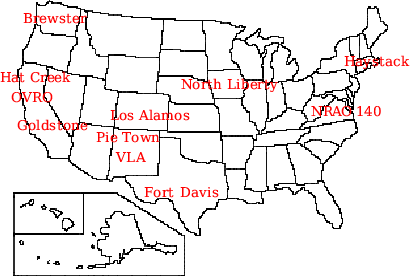
| The arrays used for the 83 VLBI experiments of this project were made by the US antennae displayed on this map. A typical array was made of 4 to 5 antennae, one of which was a large sensitive antenna, Goldstone NASA DSN 70 m (64 m) or the phased VLA 125 m, the other antennae were 25 m(VLBA), 37 m (Haystack) or 140 feet (NRAO140). |
|
|
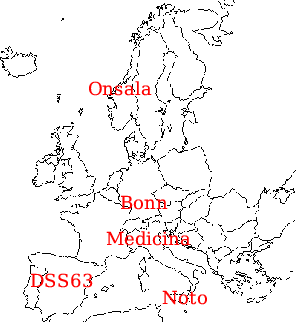
The european radiotelescopes involved in the VLBI arrays of this project were the 100 m MPI antenna at Effelsberg (near Bonn), the 70 m NASA DSN antenna near Madrid (DSS63), Medicina (32 m), Noto (32 m) and Onsala (20 m). |
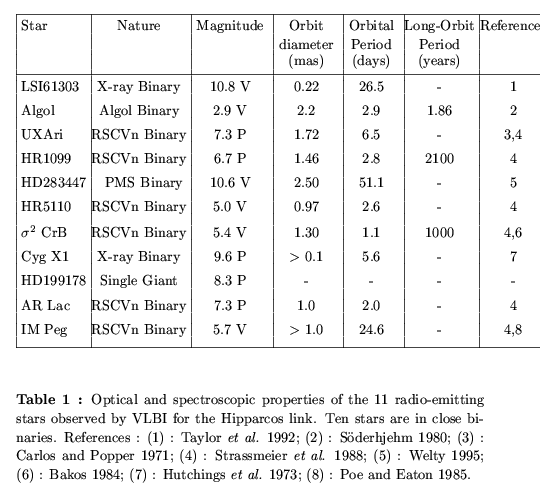
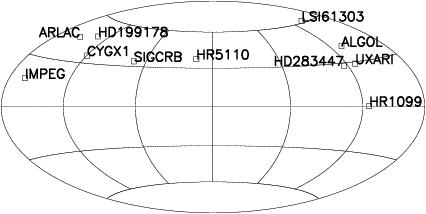
Properties and locations of the 11 radio-emitting stars observed by VLBI during this project :
| Properties of the 11 radio-emitting star observed by both Hipparcos and VLBI to tie the optical and radio coordinate systems. |
|
|
Sky distribution (equatorial coordinates) of the 11 radio-emitting stars whose coordinates at epoch (1991.25) and proper motions were used for the Hipparcos/VLBI link. |
The main steps of this project have been :
1) The first VLBI observations of radio-emitting stars on the NASA Deep Space Network and US VLB Network using the MarkIII wide-bandwidth VLBI data acquisition system of Haystack were conducted on 1982 december 19 :
2) Development of the phase-referencing technique for high-precision astrometry of weak radio sources by VLBI :
3) 13-year VLBI campaign to measure coordinates at epoch (1991.25), proper motions and trigonometric parallaxes of the 11 link stars :
4) Final step : the link parameters were computed by combining coordinates and proper motions of link stars from various techniques (Space Telescope, VLA, MERLIN, plates,....). The VLBI measurements from this VLBI project have the highest weight in this combination.